
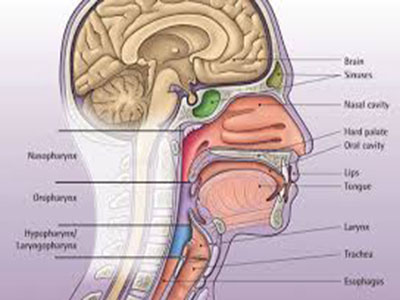





Head and Neck Cancer
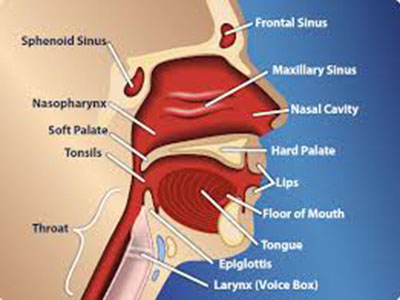
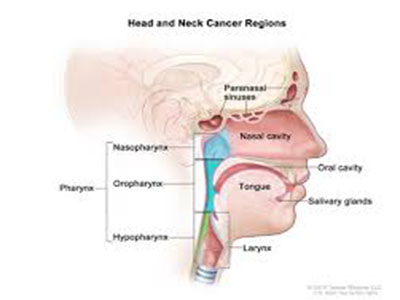
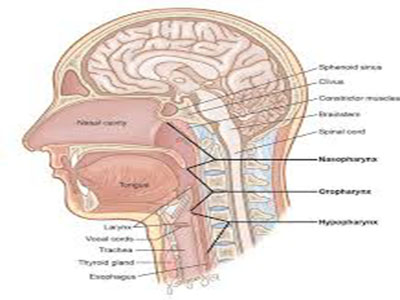
The most common type of cancer in the head and neck is squamous cell carcinoma, which arises from the cells that line the inside of the nose, mouth and throat. Squamous cell cancer is often associated with a history of smoking, or exposure to the human papilloma virus (HPV). Other less common types of head and neck cancers include salivary gland tumors, lymphomas and sarcomas. Methods of prevention include avoidance of exposure to tobacco products and vaccination of children and young adults against HPV.
Cancers spread in three main ways. The first is direct extension from the primary site to adjacent areas. The second is spread through the lymphatic channels to lymph nodes. The third is spread through the blood vessels to distant sites in the body. In head and neck cancer, a spread to the lymph nodes in the neck is relatively common.
The lymph nodes most commonly involved are located along major blood vessels underneath the sternocleidomastoid muscle on each side of the neck, particularly the internal jugular vein node at the angle of the jaw. The risk of spread to other parts of the body through the bloodstream is closely related to whether the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes in the neck, how many nodes are involved, and their location in the neck. The risk is higher if cancer is in lymph nodes in the lower part of the neck rather than only in those located in the upper neck.
The diagnosis of cancer of the head and neck is often made by a dentist, oral surgeon or physician after a patient notices symptoms such as a sore in the mouth that does not heal, or a lump in the neck. Even without symptoms, the diagnosis may be made during a routine examination.
Our Vision...
I believe in using the foreces of nature to create a medicine which utilizes these forces - applying scientific methods and adapting them in a natural way - to harm the body as little as possible. Hyperthermia fully meets this criteria
- 1
- 2
- 3
 Dr. James I. Bicher, M.D.
Dr. James I. Bicher, M.D.
Hadassah Medical School, Jerusalem, Israel
Member of National Committee on Hyperthermia. A Founder and Past President of the North American Hyperthermia Group (NAHG). Secretary and (1972-1981) President (1981) of International Society of Oxygen Transport of Tissue. Zondec Award, (Hadassah Medical School, Jerusalem), 1962. President and Founder of the American Society of Clinical Hyperthermia (ASCHO).
 Dr. Ralph S. Wolfstein, M.D.
Dr. Ralph S. Wolfstein, M.D.
University of Michigan
Former, "Acting Director, Department of Radiation Therapy Nuclear Medicine: at Cedars - Sinai Medical Center. Member in Society of Nuclear Medine, Charter Member in American College of Nuclear Physicians. Member of American Society of Therapeutic Radiology and Oncology. Member of Radiation Research Society. Charter Member of International Clinical Hyperthermia Society.
 Dr. David Bell, M.D.
Dr. David Bell, M.D.
Tulane University School of Medicine, New Orleans
PhD in mathematics from, "Brown University".Community Hospital, Long Beach, CA - Medical Director of Radiation Oncologist. Board Certified, Society Member of, "PHI BETA KAPPA & SIGMA XI".